SUBSTRATE UPTAKE AND PRODUCT EXCRETION
PD Dr. A. Burkovski, A. Wirtz, C. Trötschel, M. Follmann, J. Nettekoven
| SCIENTIFIC BACKGROUND
Transport processes play a pivotal role in cellular metabolism, e.g. for the uptake of nutrients or for the excretion of metabolic waste products. Moreover, they are also important in biotechnological processes such as the production of amino acids or vitamins by the use of bacteria. |
AIMS
Understanding and quantifying the impact of transport processes on production of amino acids and vitamins in Corynebacterium glutamicum and Escherichia coli. . Elucidation of mechanism and regulation of excretion systems as well as their physiological significance in order to use this knowledge for approaches of metabolic design. |
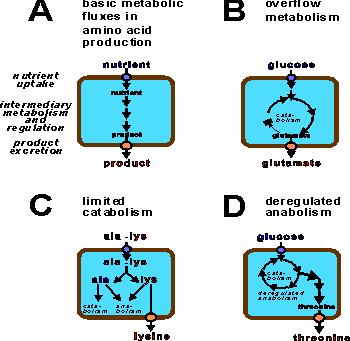 Basic metabolic situations during production of metabolites by bacteria
(A).
|
METHODS AND STRATEGY
By a combination of biochemical investigations, molecular biological and biotechnological approaches the significance of transport processes is investigated in different microorganisms. Whereas general approaches to elucidate product excretion and overflow metabolism in microorganisms are aimed to elucidate the biochemical and physiological background of these processes, specific examples need the focus on particular aspects of biosynthesis, accumulation and transmembrane transport of these solutes. While in previous projects L-glutamate, L-isoleucine, L-lysine, and riboflavin fluxes were studied, recently, pantothenate production by the use of C. glutamicum and E. coli came in the focus of research. Fluxes of its building block ß-alanine and of the product pantothenate in both organisms are characterized and mutagenesis and screening systems were established to identify the genes involved. Additionally, we are interested in the transport of the sulfur-containing amino acids L-methionine and L-cysteine. |
| FUNDING | |
|
|
|
| COOPERATION | |
|
|
|
| SELECTED PAPERS |
|